| Parameters | HDPE Corrugated Pipes | Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Length of pipes available | 6.0 m | 2.0 – 2.5 m |
| Pipe material property | Flexible pipe | Rigid pipe |
| Pipe design (structural property) |
Due to its flexibility it allows deformation in diameter as well as in joints under external load and soil natural movement and hence operates years after years without affecting the environment | Due to its rigid nature it could not deform and hence gets damaged under external load or leaks due to natural soil movement at joint. Sewer water could also leach in ground water harming the environment |
| Pipe jointing | Socket & Spigot joint with elastomeric sealing ring | 1. Coller joint with help of cement morter 2. Socket & Spigot joint with rubber ring and cement morter |
| Pipe weight | Very light | Heavy (19-20 times heavy than DWC pipes) |
| Pipe roughness coefficient |
0.009 Much higher flow rate due to less roughness coefficient and hence during design, pipe diameter requirement is less as compared to concrete & DI pipes |
0.014 Lesser flow rate due to more roughness coefficient and hence during designing, pipe diameter requirement will be higher than DWC pipe |
| Handling of pipe | Easy due to its light weight | Difficult due to its heavy weight |
| Chemical and Corrosion resistance | High chemical and corrosion resistance, especially to Hydrogen Sulphide gas, which is present in all sewer pipes, and other various harsh chemicals | Susceptible to damage from harsh chemicals and corrosion. Cement is also not resistant to Hydrogen Sulphide gas, hence Sulphate resistant cement is used during manufacture |
| Installation | Good flexibility, low requirements for foundation base for laying, good bending | High rigidity, high requirement for foundation base for laying, not easy to handle & bend, difficult to connect with other pipe |
| Pipe class | Stiffness class SN 4, SN 8 (Non-Internal Pressure Applications) | NP 1, NP 2, NP 3, NP 4 (Non-Internal Pressure Applications) |
| Pipe stacking on site | Stacked on plain ground. Smaller diameter pipes can be nested in bigger diameter pipes | Stacked on plain ground seperately. Can not be nested due to its heavy weight |
| Pipe handling on field | Light weight hence safe in manual handling, has high impact resistance and is non-breakable due to miss handling | Heavy weight hence poor safety during handling, may lead to damage due to mishandling |
| Working features | High safety under buried installation | Low safety under burried installation |
| Life time | More than 50 years | Around 15-20 years |
Feature Comparison
Flow Rate Comparison
| Size | Concrete | HDPE Corrugated Pipe | ||||||
| Flow Capacity (m3/s) at 1% Slope | Flow Capacity (m3/s) at 10% Slope | Flow Capacity (m3/s) at 1% Slope | Flow Capacity (m3/s) at 10% Slope | |||||
| at 60% fullness | at 70% fullness | at 60% fullness | at 70% fullness | at 60% fullness | at 70% fullness | at 60% fullness | at 70% fullness | |
| 225mm | 0.028 | 0.0349 | 0.0886 | 0.1104 | 0.042 | 0.0524 | 0.1329 | 0.1657 |
| 250mm | 0.0371 | 0.0462 | 0.1173 | 0.1462 | 0.0559 | 0.0696 | 0.1767 | 0.2202 |
| 300mm | 0.0603 | 0.0752 | 0.1908 | 0.2377 | 0.0905 | 0.1128 | 0.2863 | 0.3568 |
| 400mm | 0.1299 | 0.1619 | 0.4108 | 0.512 | 0.1954 | 0.2435 | 0.618 | 0.7702 |
| 500mm | 0.2356 | 0.2936 | 0.7449 | 0.9283 | 0.3548 | 0.4422 | 1.122 | 1.3983 |
| 600mm | 0.3831 | 0.4774 | 1.2113 | 1.5095 | 0.5749 | 0.7164 | 1.818 | 2.2656 |
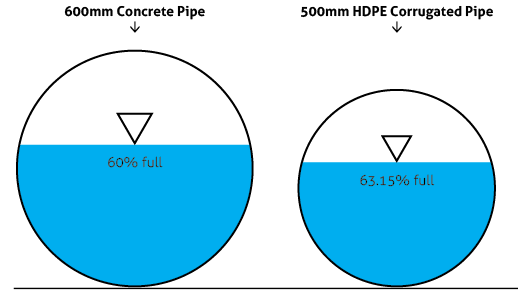
As can be seen from the table above, HDPE Corrugated Piping has a higher flow rate due to a lower roughness coefficient. Therefore, when designing the system, it is generally possible to use a smaller size in TOP-PIPE HDPE Corrugated Pipes in comparison to the same diameter of concrete pipes.
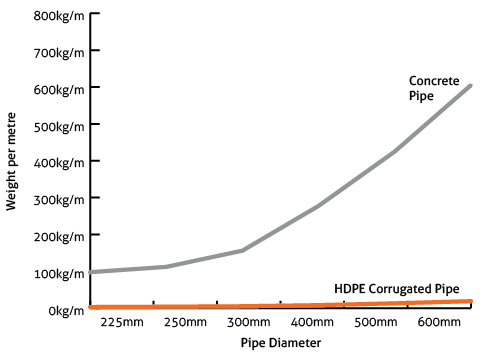
Weight Comparison
The chart on the left show the significant weight difference between TOP-PIPE HDPE Corrugated Pipes and Concrete Pipes. This means that the pipes are easier and safer to handle and make field adjustments, which reduces installation cost and time.